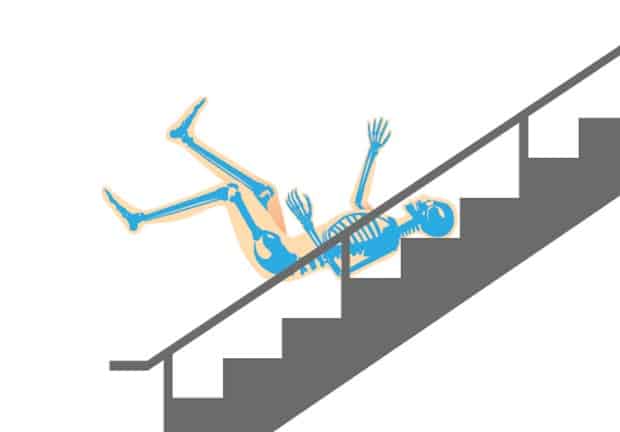

The tailbone is the lower part of the spine of 3-5 fused vertebrae, which is connected to the sacrum by an intervertebral disc. Despite the fact that it is considered a vestigial remnant of the tail, muscle fibers of the buttocks are attached to its upper section, as well as muscle ligaments that provide the functioning of the human excretory organs. Therefore, a severe injury to the tailbone can lead to serious disruption of their performance.
Classification of tailbone injuries
Falls from a slip, twist of a leg, or an unsuccessful jump often end up landing on the buttocks or lower back. In this case, trauma to the tailbone in an adult is almost inevitable. The child, due to his small mass and small stature, most often does with a slight fright.
According to the degree of damage, injuries to the tailbone are subdivided into:
- Bruises (ICD-10 S30.0) are when only muscle tissue is affected, hematomas and simply painful places appear. Severe pain is felt only at the first moment. Then it decreases or completely disappears in a calm state, and also manifests itself with tension of the lumbar muscles and after prolonged static tension of the buttocks in a sitting position. Also, pain occurs in a specific place of the bruise when you press on it.
- Dislocations and subluxations (ICD-10 S33.2) – with a strong blow or repeated damage to the coccyx, the integrity of the ligaments is disrupted and the lower sacral vertebra is displaced.
- Closed fracture (ICD-10 S32.20) – occurs without disturbing the external integument.
- Open fracture (ICD-10 S32.21) – when bone fragments or external influences damage the integrity of the skin.
Clinical picture
Often, a bruise is characterized by the absence of an obvious manifestation of damage. After the initial sharp pain during the impact, it gradually subsides and sometimes completely disappears. It may seem that everything went well, but after a while a hematoma and a painful area at the site of injury are found. Painful sensations appear when standing up, during bowel movements and long sitting on a hard surface.
In severe cases, the pain does not diminish and this most likely indicates a dislocation or fracture of the tailbone. Therefore, it is urgently required to contact a medical institution to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics
The traumatologist makes an initial assessment of the degree of damage by visual examination and palpation of the coccyx area. X-rays are taken if there are symptoms of a fracture, dislocation, or rupture of the ligaments. In the case of extensive hemorrhage and large swelling, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography can be performed. With a minor injury, a psychosomatic cause of pain in the tailbone is sometimes diagnosed. Then the patient is sent to a psychotherapist to clarify the diagnosis and further treatment.
First Aid and Risk of Injury
First aid should be provided as quickly and carefully as possible in order to prevent harm to health from repeated injury. First of all, you should lay the victim on a flat surface on his stomach. Then apply ice or a cold compress to the tailbone. Available analgesics can be used to relieve severe pain.
In case of acute pain, independent movement of the victim must not be allowed and an ambulance must be called immediately. To avoid complications with any bruises of the tailbone, you should consult a doctor.
Late initiation of treatment or its absence often leads to negative consequences. In addition to regular pain, this can create problems in sexual relations and hinder the body’s excretory functions.
Disruption of the normal functioning of the coccyx and surrounding tissues especially affects the health of women during pregnancy and often becomes the cause of difficult childbirth.
The result of an old untreated injury can be the appearance of a lump, which not only causes discomfort and over time begins to hurt constantly, but can also provoke a number of serious diseases – from spinal deformity to blood poisoning and the development of malignant tumors.
Conservative therapy methods
First of all, it is required to minimize the load on the injured area and avoid sudden movements. To do this, for two to three weeks, it is advisable to completely exclude finding the injured person in a sitting position, hot baths and warming ointments, sleep only on the side or stomach.
To reduce swelling and pain, cold compresses are applied and pain relievers, nonsteroidal drugs, gels, and ointments with a cooling effect are used. In this case, you cannot smear the edges of wounds and damaged skin areas. For their rapid healing, special means should be used. Problems with bowel movements are relieved with laxatives. Various homeopathic remedies also help to reduce edema, resorb hematomas and accelerate the recovery of the skin at the site of injury.
After stabilizing the condition and relieving the pain syndrome, warming compresses and special restorative gymnastics exercises are started to dissolve hematomas, gradually increasing the number of approaches and range of motion.
To speed up the recovery process, various physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed:
- Thermal effect – UHF, diathermy.
- Stimulation of nerve endings with special currents – electrophoresis, interference therapy, diadynamic therapy.
- Ultrasound treatment – phonophoresis.
- Therapy with ultraviolet rays – medium-wave ultraviolet radiation.
- Massotherapy.
At home, you can use alcohol compresses with various components: honey, iodine, analgin. Rubbing a combination of honey and vinegar or fir oil into the tailbone area (in the absence of skin damage), followed by wrapping the lower back with a woolen cloth, helps well.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is used only for severe injuries that cause severe internal bleeding or it is required to eliminate the inflammatory process, or the consequences of a fracture.
Prevention measures
The best prevention of such injuries is to maintain good physical condition, muscle training and coordination of movements at all times. This will avoid falls or minimize their negative consequences.
Consequences of a bruise
A fall on the buttocks, in addition to damaging the coccyx, creates an extreme shock load on the entire spine, which often causes displacement of the vertebrae in any of its parts and can have serious consequences: from increased blood pressure to paralysis of the lower extremities. Such injuries often provoke the occurrence of varicose veins and hemorrhoids. In fractures, bone fragments can damage nearby abdominal organs.
Timely medical or surgical treatment in most cases guarantees the restoration of the coccyx and surrounding tissues. Untreated bruises or sprains lead to complications and become the cause of many diseases, the cause of which can be difficult to diagnose. Therefore, it is better to start self-treatment at home even for minor bruises after consulting a traumatologist, surgeon or vertebrologist.



